Every year, an estimated 1.25 million people die, and millions more suffer injuries in road accidents. The faster a vehicle moves, the higher the risk of a crash. The World Health Organization recommends several evidence-based measures to reduce fatalities and injuries. They cite speed management with cameras as one of the most effective deterrents. Read on to find out how speed cameras work.
Speed Management Through Traffic Monitoring Cameras
Lawmakers set speed limits based on the function and design of the road and vehicle types (such as trucks versus cars). Cameras that measure speed may be fixed, portable, or mobile.
Cameras with fixed locations are predictable, and they directly influence traffic speed in a given area. The locations are determined based on accident patterns and other traffic data.
On the other hand, portable and mobile ANPR cameras can be used anywhere, even mounted on police cars. They contribute to road safety by inspiring drivers to respect traffic laws and speed limits in a general sense.
How Speed Cameras Work
When discussing how speed cameras operate, we typically refer to spot speed cameras, which detect vehicles and measure their speed at a specific point on the road. These devices rely on clever technology to automatically detect cars and measure their speed. Some use induction loops in the road, which are very accurate but can be expensive and difficult to install and the quality of the road strongly influences its lifespan. Radar is a popular choice because it’s reliable, covers more traffic lanes, and identifies the category of vehicles. Lasers are also very precise, and can be operated from a long distance, though they might struggle in bad weather. More recently, AI-powered on-board applications recognize the characteristics necessary for vehicle identification, including license plate number, nationality, make, model, category and even the color of the vehicles.
When a car drives too fast, the camera takes a photo or video. It records important details like the license plate, speed, time, date, and location. Advanced cameras can even recognize the car’s make, model, color and category (as speed limits depends in many cases on the category of the vehicle). This information is then checked to confirm the violation, and local authorities decide whether to give a warning or a fine.
Imagine a busy highway full of cars—that’s where the speed cameras really help. They watch traffic nonstop, and if someone speeds, the system immediately records it with the exact time and place. But these cameras do more than catch speeders. The data they collect also helps find dangerous spots on the road, guiding decisions like adding warning signs or speed bumps to make driving safer for everyone.
In contrast, average speed cameras monitor a vehicle’s speed over a longer distance by recording the time it takes to travel between two points, calculating the average speed to ensure compliance with speed limits.
What is Spot Speed Measurement and Average Speed Calculation?
When it comes to measuring the speed of vehicles, we distinguish between two types of speed enforcement solutions with cameras: spot speed measurement and average speed calculation. These systems work as follows:
Spot Speed Measurement
Speed cameras will measure a vehicle’s speed at a certain spot. As mentioned above, different cameras use different technologies such as laser, radar, video analytics, and more.
The disadvantage of the fixed spot speed solution is that people learn where the cameras are. Some mobile applications that aid navigation also indicate their location. They slow down as they approach the spot in question and then speed up again.
This practice undermines the main objective of consistently enforcing speed limits to reduce road accidents significantly.
Still, at locations where people have died due to drivers going too fast or through a red light, they play an undeniable role in preventing even more accidents from happening.
Adaptive Recognition’s fixed speed enforcement camera Vidar Speed is ideal for this type of setup.
For efficient and consistent speed enforcement, it is best to use fixed and portable speed cameras, such as Adaptive Recognition’s S1 mobile speed camera, simultaneously. Fixed ones to prevent violations in hazardous, accident-prone areas. Mobile ones to ensure that drivers respect speed limits in the broad sense.
Average Speed Measurement: A Growing Trend in Traffic Enforcement
Average speed measurement is gaining recognition as an effective method for encouraging safe driving habits, particularly because spot speed measurement cameras are often easy for drivers to detect and temporarily adjust their behavior to avoid penalties. By monitoring vehicle speeds over an extended road section, average speed measurement promotes consistent compliance with speed limits, fostering safer and more responsible driving patterns.
Average speed measurement works by using a pair of intelligent traffic monitoring cameras placed at two points along a road section with a consistent speed limit, typically a few hundred meters to several kilometers apart. As the vehicle enters the specific road section, an intelligent traffic monitoring camera – such as Adaptive Recognition’s entire range of cameras connected to the Globessey Data Server (GDS) – captures its number plate and timestamps the record. At the end of the road section, another traffic monitoring camera captures the vehicle’s license plate once more. To ensure accurate and reliable measurements, the road section must be precisely measured and officially certified.
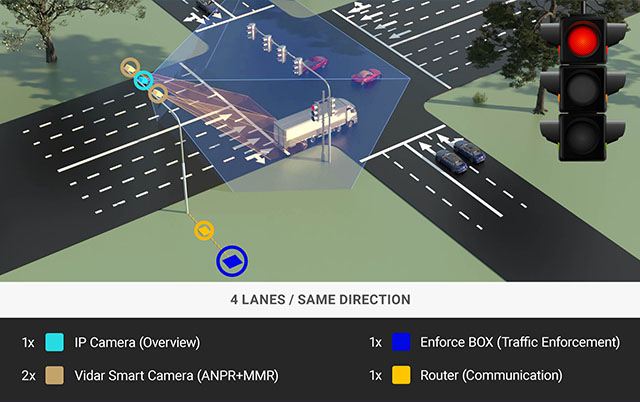
From the data on the timestamps and the length of the road, it is easy to calculate the vehicle’s average speed. Note that the two cameras do not need to have speed measurement capability. Still, they need to capture number plates, record data, and communicate with different databases. The advantage of these systems is that they can enforce speed limits over an entire stretch of road and not just one single spot.
Average speed measurement systems are particularly effective in ensuring steady speeds in critical areas like tunnels, where they help prevent high-speed collisions in confined spaces, and bridges, where they mitigate risks from abrupt speed changes in sensitive structures. They are also invaluable on long road stretches, promoting consistent compliance with speed limits, improving traffic flow, and reducing accidents.
Other Uses For Traffic Monitoring Cameras
Speed and traffic law enforcement aside, the data provided by smart traffic monitoring cameras are valuable for traffic and road usage statistics. The analysis of statistical data serves as the basis of certain traffic-related smart city solutions. For example, low-emission zones and traffic flow optimization to avoid congestion are crucial concerns when creating sustainable and healthy smart cities.
Any questions or inquiries? We’re here to support you every step of the way: